[Gut Microbiome] The contributory role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease
- e 1410
Thecontributory role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease
W.H. Wilson Tangand Stanley L. Hazen
Department ofCellular and Molecular Medicine, Lerner Research Institute, and Department ofCardiovascular Medicine, Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic,Cleveland, Ohio, USA.
제목
심혈관 질환에 기여하는 장내 미생물의 역할
내용
우리 팀은 최근 트리메틸아민 (trimethylamine)의 일부분인콜린 (choline) 및 포스파티딜 콜린 (phosphatidylcholine)그리고 L-카르니틴 (L-carnitine)을함유한 특정 식이 영양소가 죽상경화성 (atherosclerotic) 심장 질환의 발병에 기여한다는사실을 발견했다. 메타 유기체 (Meta-organismal)의경로는 장내 미생물에 의존한 TMA 형성, 숙주 내 간(肝)의 플라빈 모노산소첨가효소 3 (flavinmonooxygenase 3; FMO3)에 의존한 TMA-N-oxide (TMAO) 형성, 죽상동맥경화증 (atherosclerosis)에 기계적으로 연결되어있는 것으로 보이는 대사산물을 포함한 것으로 밝혀졌으며, 각 수준은 심혈관 질환 (CVD)의 위험과 강한 연관이 있다. 종합적으로, 이러한 연구들은 정립된 메타 유기체 경로에 따른 영양 전구체, 장내미생물 및 관련 요인들(host participants)이 CVD의예방 및 치료를 위한 새로운 표적이 될 수 있음을 나타낸다.
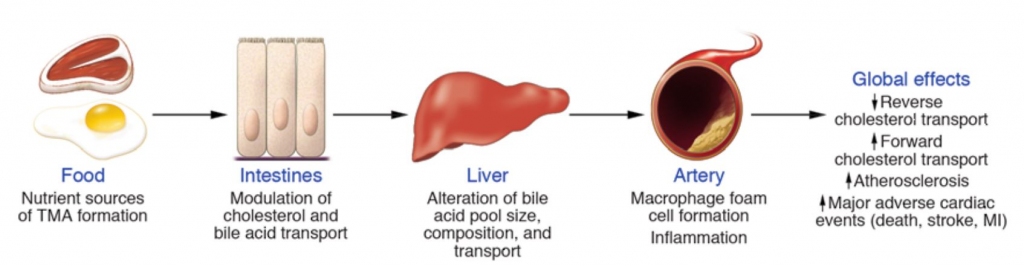
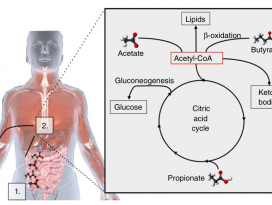
Figure 2. Effects of gut microbiota–dependent TMAO production
on cholesterol and sterol metabolism and atherosclerosis.
콜레스테롤과 스테롤(sterol) 대사및 죽상경화증에 대한 장내 미생물 의존 TMAO 생산의 효과
(TheJournal of Clinical Investigation, 2014)
Keywords
: #Trimethylamine #Phosphatidylcholine #Choline #L-carnitine #Atherosclerosis #CardiovascularDisease #CVD #AtheroscleroticHeartDisease #TMA #TMA–N-oxide
#트리메틸아민 #포스파티딜콜린 #콜린 #엘카르니틴 #죽상경화증 #심혈관계질환 #심혈관질환 #죽상경화성심장질환 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균 #마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군
[출처: Tang, W.W., & Hazen, S. L. (2014). The contributory role of gut microbiota incardiovascular disease. The Journal of clinical investigation, 124(10), 4204-4211.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.