[Gut Microbiome] Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour
- e 1392
Mind-alteringmicroorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour
John F. Cryanand Timothy G. Dinan
| Recent years have witnessed the rise of the gut microbiota as a major topic of research interest in biology. Studies are revealing how variations and changes in the composition of the gut microbiota influence normal physiology and contribute to diseases ranging from inflammation to obesity. Accumulating data now indicate that the gut microbiota also communicates with the CNS — possibly through neural, endocrine and immune pathways — and thereby influences brain function and behaviour. Studies in germ-free animals and in animals exposed to pathogenic bacterial infections, probiotic bacteria or antibiotic drugs suggest a role for the gut microbiota in the regulation of anxiety, mood, cognition and pain. Thus, the emerging concept of a microbiota–gut–brain axis suggests that modulation of the gut microbiota may be a tractable strategy for developing novel therapeutics for complex CNS disorders. |
제목
마음을 변화시키는 미생물: 장내 미생물이 뇌와 행동에 미치는 영향
내용
최근 몇 년 동안 생물학에 대한 연구 관심사의 주요 주제로서 장내 미생물의 부상이 목격되고 있다. 관련 연구들은 장내 미생물 구성의 변형 및 변화가 정상적인 생리학에 어떻게 영향을 미치며 염증에서 비만에 이르는질병들에 어떠한 방식으로 기여하는지 밝히고 있다. 축적되고 있는 여러 데이터들은 이제 장내 미생물이신경계, 내분비선 및 면역 경로를 통해 중추신경계 (CNS)와통신하여 뇌의 기능과 인간의 행동에 영향을 미칠 수 있다는 것을 가리킨다. 무균 동물과 병원균 감염, 프로바이오틱스(유익균) 또는항생제에 노출된 동물에 대한 연구는 불안, 기분 상태, 인지및 통증의 조절에 있어 장내 미생물의 역할을 시사한다. 따라서 미생물-장-뇌 축 (microbiota-gut-brain axis)이라는 새로운개념은 복잡한 CNS 장애에 대한 새로운 치료법을 개발하는 데 있어 장내 미생물을 조절하는 방법이 다루기쉬운 전략이 될 수 있음을 시사한다.
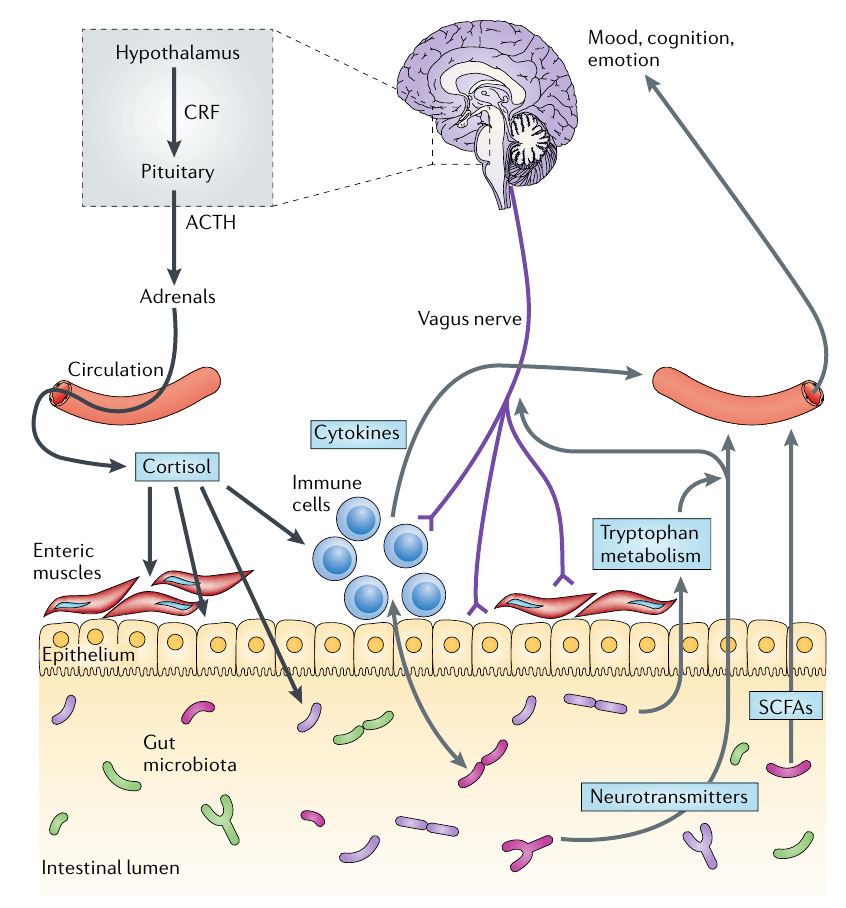
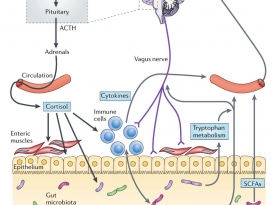
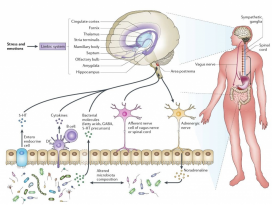
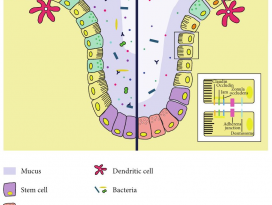
Figure 1 | Pathways involved in bidirectional communicationbetween the gut microbiota and the brain.
장내 미생물과 뇌 사이의 양방향 통신에 관여하는경로 (Nature reviews neuroscience, 2012)
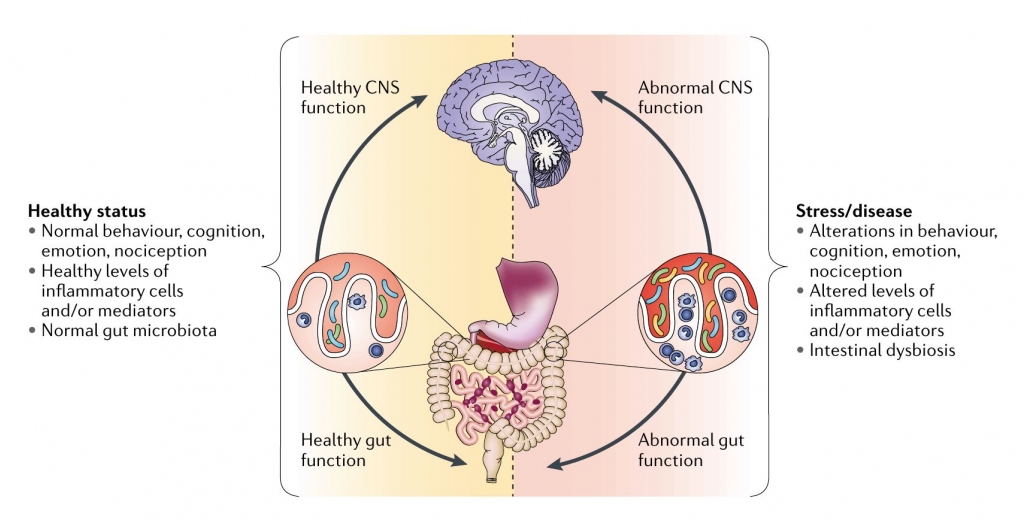
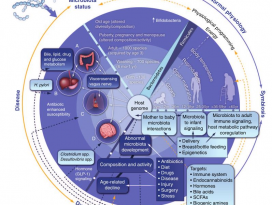
Figure 3 | Impact of the gut microbiota on the gut–brain axisin health and disease.
건강과 질병에서의 장-뇌축에 대한 장내 미생물의 영향 (Nature reviews neuroscience, 2012)
Keywords
: #Microbiome#Microorganisms#Microbes #Microbiota #GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota#GutMicrobes #Probiotics#Gut-BrainAxis #Microbiota-Gut-BrainAxis #CNS #NeuralPathways #EndocrinePathways#ImmunePathways #BrainFunction #Cognition #Behavior #AntibioticDrugs #Dysbiosis#MicrobialDysbiosis
#마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균 #장뇌축 #뇌장축 #장내미생물뇌축 #미생물장뇌축 #미생물뇌장축 #중추신경계 #신경경로 #내분비경로 #면역경로 #뇌기능 #뇌인지 #행동 #항생제 #항생약물 #장내미생물불균형 #디스바이오시스
[출처: Cryan, J.F., & Dinan, T. G. (2012). Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of thegut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nature reviews neuroscience, 13(10), 701.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.