Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review
Rout George Kerry,Jayanta Kumar Patra, Sushanto Gouda, Yooheon Park, Han-Seung Shin, GitishreeDas
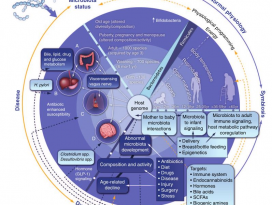
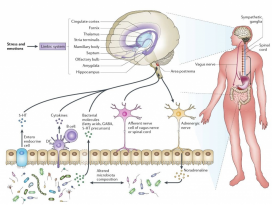
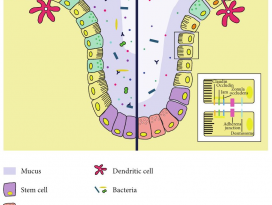
| Abstract Humans are a unique reservoir of heterogeneous and vivacious group of microbes, which together forms the human-microbiome superorganism. Human gut serves as a home to over 100-1000 microbial species, which primarily modulate the host internal environment and thereby, play a major role in host health. This spectacular symbiotic relationship has attracted extensive research in this field. More specifically, these organisms play key roles in defense function, eupepsia along with catabolism and anabolism, and impact brain-gut responses. The emergence of microbiota with resistance and tolerance to existing conventional drugs and antibiotics has decreased the drug efficacies. Furthermore, the modern biotechnology mediated nano-encapsulated multiplex supplements appear to be high cost and inconvenient. Henceforth, a simple, low-cost, receptive and intrinsic approach to achieve health benefits is vital in the present era. Supplementation with probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics has shown promising results against various enteric pathogens due to their unique ability to compete with pathogenic microbiota for adhesion sites, to alienate pathogens or to stimulate, modulate and regulate the host's immune response by initiating the activation of specific genes in and outside the host intestinal tract. Probiotics have also been shown to regulate fat storage and stimulate intestinal angiogenesis. Hence, this study aims to underline the possible beneficial impact of probiotics for human health and medical sectors and for better lifestyle. |
제목
인체 건강에 유익을 주는 프로바이오틱스: 리뷰
내용
추상
인간은 인간 - 미생물의 초미생물 (superorganism)을함께 형성하는 미생물군의 이질적이고 활동감 있는 독특한 저장고이다. 인간의 장은 주로 100개~1000개 이상의 미생물 종의 서식지로, 주로 내부 환경을 조절하여 숙주의 건강에 중요한 역할을 한다. 이러한놀라운 공생 관계는 해당 분야에서 광범위한 연구를 이끌어 냈다. 보다 구체적으로 말하면, 이러한 미생물은 방어 기능, 동화작용 및 이화작용에 따른 정상 소화(eupepsia)에 중요한 역할을 하고 뇌-장 (brain-gut) 반응에 영향을 준다. 기존의 현대 약물 및 항생제에저항성과 내성을 지닌 미생물의 출현은 약물의 효능을 감소시켰다. 나아가 현대의 생명 공학을 통한 나노캡슐 멀티플렉스 보충제는 고비용과 불편함이 있는 것으로 보인다. 그러므로 이제부터 현 시대에서는 건강혜택을 얻기 위한 간단하고 저비용이며 수용적이고 내재적인 접근법이 필수적이다. 프로바이오틱스, 프리바이오틱스 및 신바이오틱스의 보충은 이들이 정착할 곳을 위해 병원균과 경쟁하고 소외시키거나, 특정 유전자의 활성화가 일어나게끔 함으로써 숙주의 면역 반응을 자극 및 조절하는 독특한 능력으로 인해 다양한장내 병원균에 맞서는 유망한 결과를 보였다.
프로바이오틱스는 또한 체지방 축적을 조절하고 장내 혈관 신생을 자극하는 것으로 나타났다. 따라서 본 연구는 인체 건강 및 의료 분야, 그리고보다 나은 생활방식에 대한 프로바이오틱스의 잠재적인 유익한 영향을 강조하는 것을 목표로 한다.
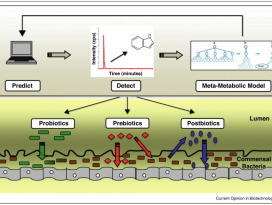
내용 발췌 (정의 및 종류)
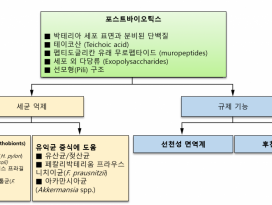
l 포스트바이오틱스
1) 정의: 포스트바이오틱스는 숙주 안에서 생물학적 활성을 갖는 프로바이오틱스의박테리아 생성물 또는 대사산물 (metabolic byproducts)이다.
2) 종류: 일반적으로 포스트바이오틱스는박테리오신 (bacteriocins), 유기산 (organicacids), 에탄올 (ethanol), 디아세틸 (diacetyl),아세트 알데히드 (acetaldehydes) 및 과산화수소(hydrogen peroxide)와 같은 대사산물을 포함하지만, 일부열처리 살균 (heat-killed probiotics) 또한 숙주에서 생물학적 활성을 발휘할 수 있는중요한 박테리아 구조를 유지할 수 있음이 밝혀졌다.
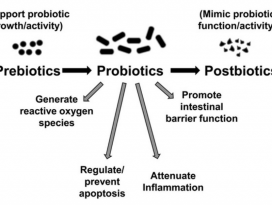
l 프리바이오틱스
1) 정의: 인체 내에서 쉽게소화되지는 않지만 장내에서 유익균(프로바이오틱스)의 성장또는 활성을 자극하는데 있어 선택적 역할을 하는, 장내 미생물총 (gutmicrobial flora)을 변화시키는 특정 영양소
2) 종류: 프리바이오틱스에는인슐린, 프락토올리고당 (oligofructose), 자당에서합성된 프락토올리고당 (fructo-oligosaccharides, FOS)뿐만 아니라 갈락토오스 올리고당(galactose-containing oligosaccharides) 및 자일로오스 올리고당 (xylose-containing oligosaccharides)의 비피더스 특성 (bifidogenic: 장내에서 비피더스균의 증식에 도움이 되는)이포함된다.
l 신바이오틱스
1) 정의: 프로바이오틱스와 프리바이오틱스제품의 결합
2) 종류: 신바이오틱스는 생균함유 보충제의 장내 생존과 정착을 향상시키는 데 도움이 된다. 시너지 효과는 프로바이오틱스와 프리바이오틱스가모두 살아있는 체계에서 함께 작용할 때 보다 효율적으로 발휘된다.
Keywords
: #Microbiome#Microorganisms#Microbes #Microbiota #GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota#GutMicrobes #Probiotics#Prebioitcs #Synbiotics #Postbiotics #MetabolicByproducts #Metabolites #Symbiotic
#마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균 #프리바이오틱스 #신바이오틱스 #포스트바이오틱스 #대사산물 #신진대사산물 #대사부산물 #공생
[출처: Kerry, R.G., Patra, J. K., Gouda, S., Park, Y., Shin, H. S., & Das, G. (2018).Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. Journal of foodand drug analysis, 26(3), 927-939.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.