[Lactobacillus gasseri] Effect of fermented milk-based probiotic preparations on Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
- e 1689
Effect of fermented milk-based probiotic preparations on
Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review and
meta-analysis ofrandomized-controlled trials
Aarti Sachdeva andJitender Nagpal
Department of ClinicalEpidemiology, Sitaram Bhartia Institute of Science and Research, New Delhi,India
| Objective To evaluate the effect of fermented milk-based probiotic preparations on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Design Systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Data sources Electronic databases and hand search of reviews, bibliographies of books and abstracts and proceedings of international conferences. Review methods Included trials had to be randomized or quasi-randomized and controlled, using fermented milkbased probiotics in the intervention group, treating Helicobacter-infected patients and evaluating improvement or eradication of H. pylori as an outcome. Results The search identified 10 eligible randomized controlled trials. Data were available for 963 patients, of whom 498 were in the treatment group and 465 in the control group. The pooled odds ratio (studies n = 9) for eradication by intention-to-treat analysis in the treatment versus control group was 1.91 (1.38–2.67; P < 0.0001) using the fixed effects model; test for heterogeneity (Cochran’s Q = 5.44; P = 0.488). The pooled risk difference was 0.10 (95% CI 0.05–0.15; P < 0.0001) by the fixed effects model (Cochran’s Q = 13.41; P = 0.144). The pooled odds ratio for the number of patients with any adverse effect was 0.51 (95% CI 0.10–2.57; P = 0.41; random effects model; heterogeneity by Cochran’s Q = 68.5; P < 0.0001). Conclusion Fermented milk-based probiotic preparations improve H. pylori eradication rates by approximately 5–15%, whereas the effect on adverse effects is heterogeneous. |
제목
발효유 기반의 프로바이오틱 조제용 물질(Probioticpreparations) 헬리코박터 파일로리(Helicobacterpylori)
박멸에 미치는 영향:무작위 통제 시험의 체계적인 검토 및 메타 분석
내용
목표
헬리코박터 파일로리(Helicobacterpylori) 박멸에 관한 발효유 기반 프로바이오틱 제제의 효과를 평가하고자 한다.
디자인
무작위 통제 시험의 체계적인 재검토
데이터 소스
전자 데이터베이스 및 수작업을 통한 학술논평 검색,도서 및 초록 등의 참고문헌,국제 회의 진행 결과
방법 검토
포함된 임상 시험은 중재 그룹에서 발효유 기반 프로바이오틱스를 사용하고,헬리코박터에 감염된 환자를 치료하고
H. pylori의개선 또는 박멸을 결과로써 평가하는데 있어 무작위화 또는 준 무작위화 및 통제가 필요했다
.
결과
해당 탐구에서 10가지의 적격 무작위 통제 시험이 확인되었다.963명의 환자에 대한 자료가 이용 가능하였고,
그 중498명은 치료군,465명은 대조군으로 나뉘었다.치료군 VS 대조군에서 ITT(intention-to-treat)분석에 의한
박멸의 풀드 오즈비(pooledodds ratio)(n = 9)는고정 효과 모델(fixedeffects model)을 사용했을 때1.91이었다
(1.38-2.67;P <0.0001); 이질성 테스트 (Cochran 's Q = 5.44, P = 0.488). 고정 효과 모델에 의한 합병 위험 차이
(pooledrisk difference)는 0.10이었다(95 % CI 0.05-0.15; P<0.0001) (Cochran 's Q = 13.41, P = 0.144).
부작용이 있는 환자 수에 대한 풀드 오즈비는0.51이었다.(95 % CI 0.10-2.57, P = 0.41, 무작위 효과 모델,
Cochran 's Q 테스트에 의한 이질성=68.5, P <0.0001).
결론
발효유를 기반으로 한 프로바이오틱 조제용 물질은H. pylori 제균율을 약5-15 % 향상시켰지만,
부작용에 대한 효과는 이질적이다.
Keywords
: #FermentedMilk #Helicobacter#HelicobacterPylori #H.pylori #Meta-analysis #Yogurt #Probiotics #Microbiome#GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota
#발효유 #헬리코박터 #헬리코박터파일로리 #H.파일로리 #메타분석 #요거트 #요구르트 #유산균 #프로바이오틱스
#유익균 #마이크로바이옴 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군
[출처: Sachdeva,A., & Nagpal, J. (2009). Effect of fermented milk-based probioticpreparations on Helicobacter pylori eradication:
a systematic review andmeta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. European Journal ofGastroenterology & Hepatology, 21(1), 45–53.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
| 40 |  | 1063 | |
| 39 |  | 1045 | |
| 38 |  | 1019 | |
| 37 | 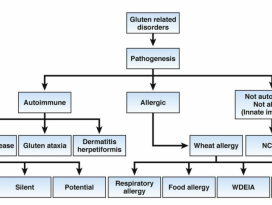 | 1127 | |
| 36 | 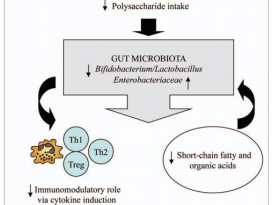 | [Gluten] Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult humans | 1039 |
| 35 |  | [Gluten] Gluten-sensitive enteropathy and functional dyspepsia | 1057 |
| 34 |  | 1029 | |
| 33 |  | [Gluten] Wheat Gluten Causes Dendritic Cell Maturation and Chemokine Secretion | 1079 |
| 32 |  | [Gluten] Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: The New Frontier of Gluten Related Disorders | 1046 |
| 31 |  | 1132 | |
| 30 |  | 1129 | |
| 29 |  | 1968 | |
| 28 |  | 2082 | |
| 27 |  | 2270 | |
| 26 | 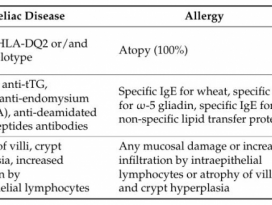 | 2413 | |
| 25 |  | [Gluten] Non-coeliac gluten sensitivity - A new disease with gluten intolerance | 1662 |
| 24 |  | 1852 | |
| 23 |  | 1689 | |
| 22 |  | 1775 | |
| 21 |  | 2511 |
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.
