Nonceliacgluten sensitivity
Alessio Fasano, AnnaSapone, Victor Zevallos, Detlef Schuppan
Mucosal Immunologyand Biology Research Center andCenter Children, Harvard Medical School, Boston,Massachusetts; for Celiac Research, Massachusetts General Hospital for Center,Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts; Division Institute ofGastroenterology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Immunotherapy, University ofMainz Medical Center, Mainz, Germany
| During the past decade there has been an impressive increase in popularity of the gluten-free diet (GFD)—now the most trendy alimentary habit in the United States and other countries. According to recent surveys, as many as 100 million Americans will consume gluten-free products within a year. Operating under the concept that the GFD benefits only individuals with celiac disease, health care professionals have struggled to separate the wheat from the chaff; there are claims that eliminating gluten from the diet increases health and helps with weight loss, or even that gluten can be harmful to every human being. However, apart from unfounded trends, a disorder related to ingestion of gluten or gluten-containing cereals, namely nonceliac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), has resurfaced in the literature, fueling a debate on the appropriateness of the GFD for people without celiac disease. Although there is clearly a fad component to the popularity of the GFD, there is also undisputable and increasing evidence for NCGS. However, we require a better understanding of the clinical presentation of NCGS, as well as its pathogenesis, epidemiology, management, and role in conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, chronic fatigue, and autoimmunity. Before we can begin to identify and manage NCGS, there must be agreement on the nomenclature and definition of the disorder based on proper peer-reviewed scientific information. We review the most recent findings on NCGS and outline directions to dissipate some of the confusion related to this disorder. |
제목
비셀리악 글루텐 민감성
내용
지난 10년간 글루텐 프리 식단(GFD)의 인기가 인상적으로 증가했다. 현재 GFD는미국 및 기타 다른 국가에서 가장 트렌디하고 인기있는 식생활 습관이다. 최근 설문 조사에 따르면, 1년 이내에 1억 명 이상의 미국인들이 글루텐 프리 제품을 소비할것이라고 한다. 이러한 GFD가 셀리악병을 앓고 있는 사람에게만도움이 된다는 개념 하에 이용되는 상황에서, 건강 관리 전문가들은 밀을 겨에서 분리하는 데 고군분투해왔다. 식단에서 글루텐을 제거하면 건강이 증진되고 체중 감소에 도움이 된다거나, 심지어는글루텐이 모든 인간에게 해로울 수 있다는 주장들이 존재한다. 그러나 근거 없는 추세를 제외하고 글루텐혹은 글루텐 함유 곡물의 섭취와 관련된 질환, 즉 비셀리악 글루텐 민감성 (non-celiac gluten sensitivity; NCGS)이 문헌에 재등장하여 셀리악병이 없는 사람들에대한 GFD의 적절성에 대한 논의에 불을 붙였다. GFD의인기에 대한 유행 요소가 분명히 있지만, NCGS에 대한 부인할 수 없는 증거 또한 증가하고 있다. 그러나 우리는 과민성 대장 증후군, 만성 피로 및 자가 면역과 같은상태에서 NCGS의 병인, 역학, 관리 및 역할뿐만 아니라 임상적 발현에 대한 더 나은 이해가 필요하다.NCGS를 진단하고 관리를 시작하기 전에 적절한 동료 검토 과학 정보에 기반한 질환의 명명법 및 정의에 대한 합의가 있어야 한다. 우리는 NCGS에 대한 가장 최근의 연구 결과를 검토하고 해당 질환과관련된 혼란의 일부를 잠재우기 위한 방향성의 개요을 제시한다.
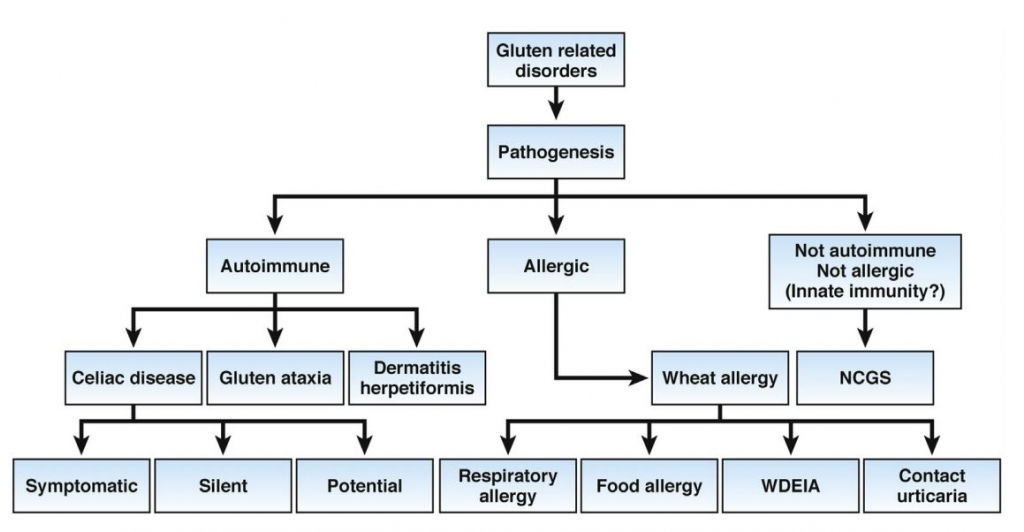
Figure 1. Classification of gluten-related disorders. WDEIA,wheat-dependent induced anaphylaxis.
글루텐 관련 질환의 분류. WDEIA, 밀 의존성 아나필락시스 유도. (Gastroenterology,2015)
Keywords
: #Gluten #Wheat #Allergy #GlutenAllergy#WheatAllergy #CeliacDisease #FODMAP #IBS #GlutenSensitivity #Autoimmunity #Anaphylaxis#GlutenFree #GlutenFreeDiet #GFD #NonCeliacGlutenSensitivity #NCGS#GlutenIntolerance #Microbiome #Microorganisms #Microbes #Microbiota#GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota #GutMicrobes #Probiotics
#글루텐 #밀#밀가루 #알러지 #글루텐알러지 #밀알러지 #셀리악병 #포드맵 #과민성대장증후군 #글루텐민감성 #글루텐과민성 #글루텐감수성 #자가면역 #아나필락시스 #글루텐프리 #글루텐프리식단 #비셀리악글루텐민감성 #글루텐불내증 #마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균
[출처: Fasano, A.,Sapone, A., Zevallos, V., & Schuppan, D. (2015). Nonceliac glutensensitivity. Gastroenterology, 148(6), 1195-1204.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
| 40 |  | 1063 | |
| 39 |  | 1045 | |
| 38 |  | 1019 | |
| 37 |  | 1128 | |
| 36 |  | [Gluten] Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult humans | 1039 |
| 35 |  | [Gluten] Gluten-sensitive enteropathy and functional dyspepsia | 1057 |
| 34 |  | 1029 | |
| 33 |  | [Gluten] Wheat Gluten Causes Dendritic Cell Maturation and Chemokine Secretion | 1080 |
| 32 |  | [Gluten] Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: The New Frontier of Gluten Related Disorders | 1046 |
| 31 |  | 1133 | |
| 30 |  | 1131 | |
| 29 |  | 1968 | |
| 28 |  | 2082 | |
| 27 |  | 2270 | |
| 26 |  | 2414 | |
| 25 |  | [Gluten] Non-coeliac gluten sensitivity - A new disease with gluten intolerance | 1662 |
| 24 |  | 1856 | |
| 23 |  | 1690 | |
| 22 |  | 1776 | |
| 21 |  | 2511 |
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.
