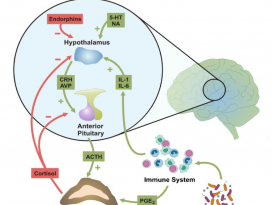
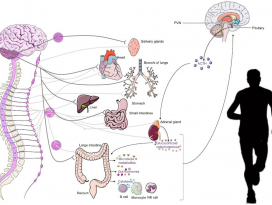
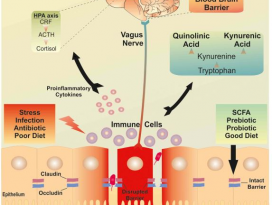
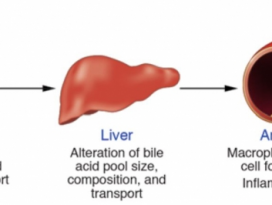
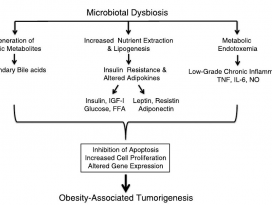
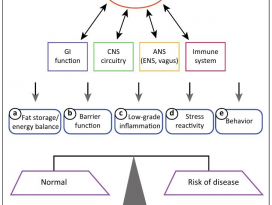
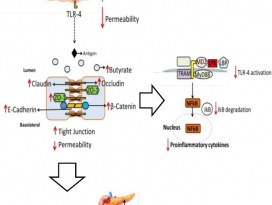
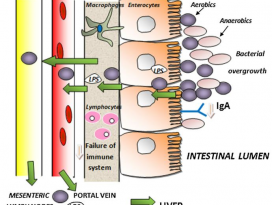
[Gut Microbiome] Pediatric obesity is associated with an altered gut microbiota and discordant shifts in Firmicutes populations
- e 1977
Pediatric obesity is associated with an altered gutmicrobiota and discordant shifts in Firmicutes populations
Alessandra Riva, Francesca Borgo, Carlotta Lassandro, ElviraVerduci, Giulia Morace, Elisa Borghi and David Berry
Department of Microbiology and Ecosystem Science, Division ofMicrobial Ecology, Research Network Chemistry Meets Microbiology, University ofVienna, Althanstrasse 14, Vienna, Austria., Department of Health Sciences, Universita degli Studi di Milano, viadi Rudin ı, 8, Milan, Italy., Department of Pediatrics, San Paolo Hospital, via di Rudin ı, 8,Milan, Italy.
| An altered gut microbiota has been linked to obesity in adulthood, although little is known about childhood obesity. The aim of this study was to characterize the composition of the gut microbiota in obese (n 5 42) and normal-weight (n 5 36) children aged 6 to 16. Using 16S rRNA gene-targeted sequencing, we evaluated taxa with differential abundance according to age- and sex-normalized body mass index (BMI z-score). Obesity was associated with an altered gut microbiota characterized by elevated levels of Firmicutes and depleted levels of Bacteroidetes. Correlation network analysis revealed that the gut microbiota of obese children also had increased correlation density and clustering of operational taxonomic units (OTUs). Members of the Bacteroidetes were generally better predictors of BMI z-score and obesity than Firmicutes, which was likely due to discordant responses of Firmicutes OTUs. In accordance with these observations, the main metabolites produced by gut bacteria, short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), were higher in obese children, suggesting elevated substrate utilisation. Multiple taxa were correlated with SCFA levels, reinforcing the tight link between the microbiota, SCFAs and obesity. Our results suggest that gut microbiota dysbiosis and elevated fermentation activity may be involved in the etiology of childhood obesity. |
Out of ‘Discussion’…
Elevated fecal concentrations of total or individualSCFAs might result from increased microbial production, shifts in microbialcross-feeding patterns, or low mucosal absorption.
제목
소아 비만은 변화된 장내 미생물 및 퍼미쿠테스 군의 부조화된 변화와연관이 있다.
내용
변화된 장내 미생물은 성인의 비만과 관련 있지만, 아동기의 비만에 대해서는거의 알려지지 않았다. 이 연구의 목적은 6세에서 16세 사이의 비만 아동(n=42) 및 정상 체중 아동(n=36)의 장내 미생물의 구성을 특성화 하는 것이었다. 16S rRNA 유전자표적서열분석을 이용하여, 연령 및 성별을 기반으로 표준화한 신체질량지수(BMI 표준지수)에 따라 차별적이고 다양한 분류군들을 평가하였다. 비만은 퍼미쿠테스(Firmicutes)의 증가 및 박테로이데테스(Bacteroidetes)의 감소로 규명되는 변화된 장내 미생물과 관련이 있었다. 상관 관계 네트워크 분석(Correlation networkanalysis)을 한 결과, 비만 아동의 장내 미생물에서도 OTUs(Operational Taxonomic Units)의 상관 밀도(correlationdensity)와 군집화(clustering)가 증가한 것으로 밝혀졌다. 박테로이데테스의 구성원은 일반적으로 BMI 표준지수 및 비만을 위한더 나은 예측 변수이며, 그 이유는 퍼미쿠테스 OTUs의부조화스러운 응답 때문일 가능성이 높다. 이러한 관찰 결과에 따르면,장내 미생물에 의해 생성된 주요 대사산물인 단쇄지방산(SCFAs; Short Chain Fatty Acids)의분변 내 농도는 비만 아동에서 더 높았으며, 이는 기질 활용의 증가를 시사한다. (추가: 논문의 토의(Discussion)부분에 의하면, 전체 또는 개별 SCFAs의분변 내 농도의 증가는 미생물 생성의 증가, 미생물 간 교차섭취 패턴의 변화 또는 점막 흡수 기능 저하로인한 것일 수 있다.) 다중 분류군은 SCFAs의 수준과상관 관계가 있었고, 미생물 및 SCFAs와 비만 간의 긴밀한연관성을 견고히 했다. 우리의 결과는 장내 미생물의 불균형 및 퍼미쿠테스군의 부패(fermentation)가 아동비만의 병인에 관여할 수 있음을 시사한다.
Keywords
: #GutMicrobiota #GutMicrobiome #Microbiome #PediatricObesity #ChildhoodObesity #Obesity #BMI #ShortChainFattyAcids #SCFA #SCFAs #NextGenerationSequencing #Bacteroidetes #Firmicutes
#장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #마이크로바이옴 #미생물군 #미생물총 #소아비만 #아동비만 #비만 #단쇄지방산 #짧은사슬지방산 #박테로이데테스 #퍼미쿠테스 #차세대염기서열분석
[출처: Riva, A., Borgo, F., Lassandro, C., Verduci,E., Morace, G., Borghi, E., & Berry, D. (2017). Pediatric obesity isassociated with an altered gut microbiota and discordant shifts in F irmicutespopulations. Environmental microbiology, 19(1), 95-105.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.