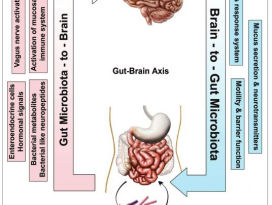
[Gut Microbiome] Gut–brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression
- e 2059
Gut–brainaxis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression
Jane A. Foster andKaren-Anne McVey Neufeld
Department ofPsychiatry and Behavioural Neurosciences, McMaster University, at St. Joseph’sHealthcare, 50 Charlton Ave. E, T3308, Hamilton, ON, L8N 4A6, Canada
| Within the first few days of life, humans are colonized by commensal intestinal microbiota. Here, we review recent findings showing that microbiota are important in normal healthy brain function. We also discuss the relation between stress and microbiota, and how alterations in microbiota influence stress-related behaviors. New studies show that bacteria, including commensal, probiotic, and pathogenic bacteria, in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract can activate neural pathways and central nervous system (CNS) signaling systems. Ongoing and future animal and clinical studies aimed at understanding the microbiota–gut–brain axis may provide novel approaches for prevention and treatment of mental illness, including anxiety and depression. |
제목
장-뇌 축(Gut–brain axis):마이크로바이옴이 불안과 우울증에 영향을 주는 방식
내용
인간의 장에서는 우리가 태어난 직후부터 며칠 이내에 공생하며 살아가는 장내 미생물총이 집단 서식을 시작한다. 본 연구에서 우리는 정상적인 건강한 뇌 기능에 있어서 미생물이 중요하다는 최근의 연구 결과를 검토한다. 우리는 또한 스트레스와 미생물의 관계, 그리고 미생물의 변화가 스트레스관련 행동에 어떻게 영향을 미치는지에 대해서도 논의한다. 새로운 연구에 따르면 위장관(GI)에서 공생 균주, 프로바이오틱스(유익균) 및 병균을 비롯한 미생물들이 신경 경로(neural pathways)와 중추신경계(CNS) 신호 체계를 활성화할수 있다고 한다. 현재 진행중이거나 향후 예정인 미생물총-장-뇌 축(The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis)의 이해를목표로 하는 동물 실험 및 임상 연구는 불안과 우울증을 포함한 정신 질환의 예방 및 치료를 위한 새로운 접근법을 제공할 수 있다.
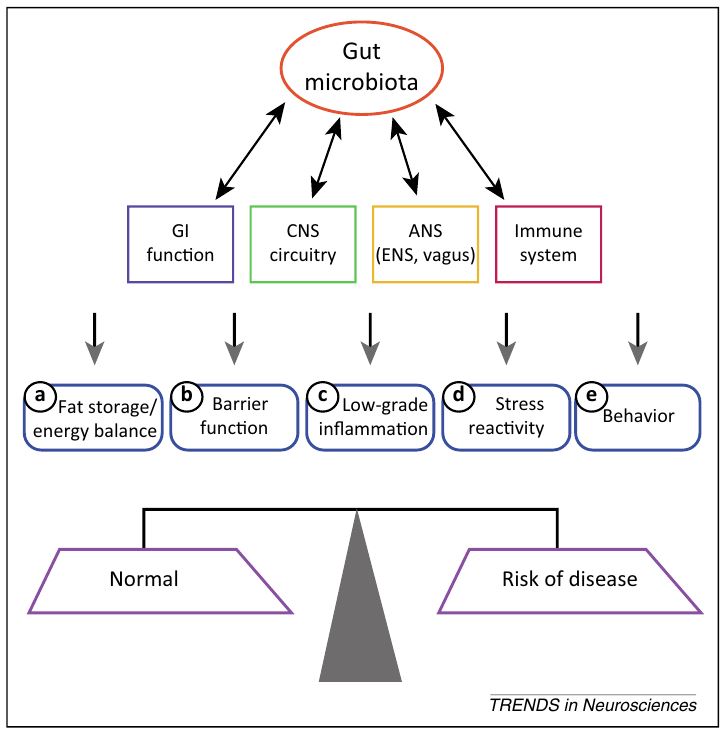
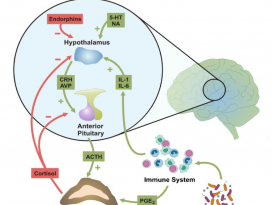
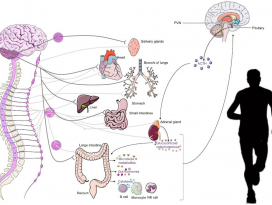
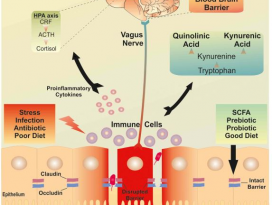
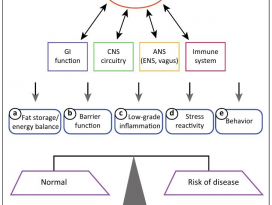
Figure 1. Bidirectional communication between gut microbiotaand components of the gut–brain axis
influence normal homeostasis and maycontribute to risk of disease.
장내 미생물총과 장-뇌 축의 구성 요소 간의 양방향 소통은 정상적인 항상성(homeostasis)에 영향을 미치고
질병의 위험에 기여할 수 있다.(
Keywords
: #Gut–BrainAxis #Microbiota–Gut–BrainAxis# Microbiome–Gut–BrainAxis #Probiotics #Microbiome #Microorganisms #Microbes#GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota #Homeostasis
#장뇌축 #장두뇌축 #뇌장축 #두뇌장축 #미생물장뇌축 #미생물총장뇌축 #미생물군장뇌축 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균 #마이크로바이옴 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #항상성
[출처: Foster, J. A., & Neufeld, K. A. M. (2013).Gut–brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends in neurosciences, 36(5), 305-312.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.