[Gut Microbiome] The Microbiome and Obesity—An Established Risk for Certain Types of Cancer
- e 1544
TheMicrobiome and Obesity—An Established Risk for Certain Types of Cancer
Connie J. Rogers,MPH, PhD, Kumble Sandeep Prabhu, PhD, and Matam Vijay-Kumar, PhD
| Obesity is a major modifiable risk factor for the development of numerous types of cancer. Although many factors contribute to obesity-driven tumorigenesis, this review focuses on the functioning of the gut microbiota (the microbiome) as an environmental risk factor for certain types of cancers, and presents possible biological mediators. Obesity is a well-studied condition that is associated with microbiotal dysbiosis, which could result in several physiologic changes that may contribute to the relationship between obesity and cancer risk. These include altered microbial metabolism, which contributes to the generation of procarcinogenic toxic metabolites; increased extraction of energy and nutrient availability leading to metabolic dysregulation that contributes to tumor growth; and/or the induction of subclinical inflammation initiating tumorigenesis. Thus, the gut microbiota may serve as a key link between obesity and cancer and, therefore, viable strategies to alter the microbiota may provide novel therapeutics to reduce obesity-associated cancer risk. |
제목
마이크로바이옴과 비만 - 특정 유형의 암에 대한 공인된 위험
내용
비만은 많은 유형의 암 발병에 있어 변경 가능한 주요 위험 요소이다. 많은요인들이 비만으로 인한 종양 형성에 기여하지만, 이 리뷰는 특정 유형의 암에 대한 환경적 위험 요인으로서의장내 미생물총(마이크로바이옴)의 기능에 중점을 두고 가능한생물학적 매개체를 제시한다. 비만은 장내 미생물총 불균형(dysbiosis)와관련되어 있다는 사실은 잘 알려져 있으며, 비만과 암 위험 사이의 관계에 기여할 수 있는 몇 가지 생리학적변화를 초래할 수 있다. 여기에는 발암성 독성 대사 산물의 생성, 종양성장에 기여하는 대사 조절 장애로 이끄는 에너지 및 영양소 이용 가능성 증가, 그리고(또는) 초기 종양 형성에 관여하는 준 임상 염증의 유도에 기여하는변형된 미생물 대사가 포함된다. 그러므로, 장내 미생물은비만과 암 사이의 중요한 연결 고리 역할을 할 수 있으며, 따라서 미생물을 변화시킬 수 있는 실행 가능한전략은 비만 관련 암의 위험을 줄이기위한 새로운 치료법을 제공할 수 있다.
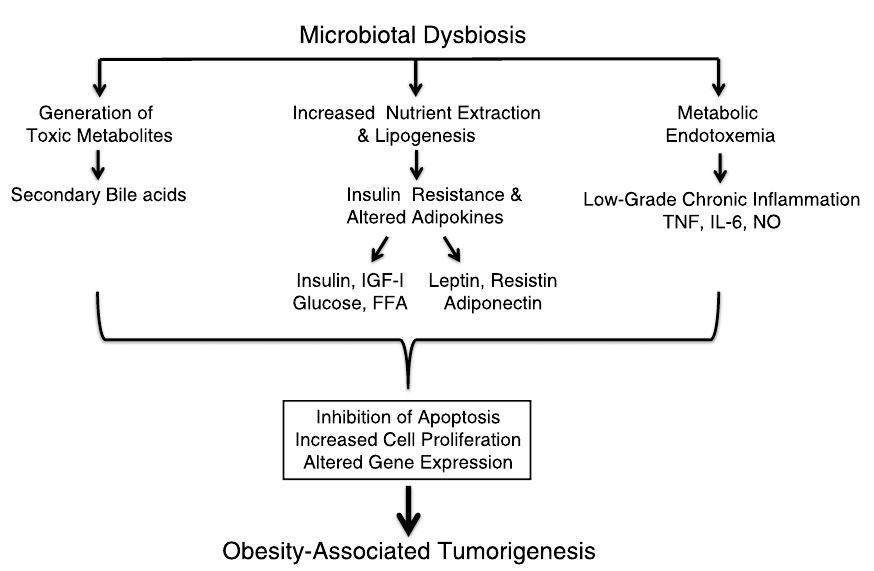
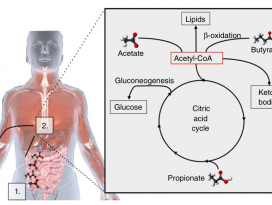
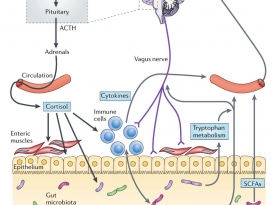
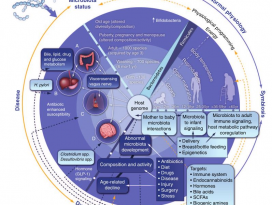
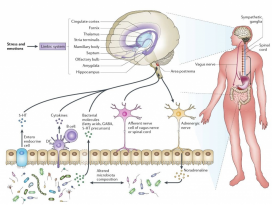
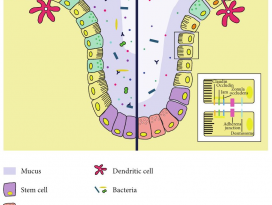
FIGURE 1. Potential mechanisms linking the microbiota,obesity, and cancer.
미생물과 비만, 암을 연결하는 잠재적 메커니즘. (TheCancer Journal, 2014)
Key Words
: #Microbiome #Microbiota #Microorganisms #Microbes#GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota, #Carcinogenesis #Cancer #MicrobialMetabolism #MetabolicDysfunction#MetabolicDysregulation #MicrobiotalDysbiosis #Dysbiosis #Inflammation #Tumor#Tumorigenesis #Obesity-Cancer #Obesity-associatedCancer #ObesityAndCancer
#마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #발암 #암발병 #암 #미생물대사 #대사기능장애 #대사장애 #대사조절장애 #장내미생물불균형 #장내미생물총불균형 #디스바이오시스 #염증 #종양형성 #종양발생 #비만과암 #비만관련암
[출처: Rogers, C.J., Prabhu, K. S., & Vijay-Kumar, M. (2014). The microbiome and obesity—anestablished risk for certain types of cancer. The Cancer Journal, 20(3),176-180.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.