[Gut Microbiome] Gut Microbiota Orchestrates Energy Homeostasis during Cold
- e 1453
Gut Microbiota Orchestrates Energy Homeostasis during Cold
Claire Chevalier, OzrenStojanovic, Didier J. Colin, Nicolas Suarez-Zamorano, Valentina arallo, ChristelleVeyrat-Durebex, Dorothée Rigo, Salvatore Fabbiano, Ana Stevanovic, StefanieHagemann, Xavier Montet, Yann Seimbille, Nicola Zamboni, Siegfried Hapfelmeier,and Mirko Trajkovski
Department of CellPhysiology and Metabolism, Centre Médical Universitaire (CMU), Faculty ofMedicine, University of Geneva, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland; Diabetes Centre,Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland; Centre forBioMedical Imaging (CIBM), Geneva University Hospitals, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland;Institute for Infectious Diseases, University of Bern, 3010 Bern, Switzerland; Divisionof Radiology, Geneva University Hospitals, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland; Institutefor Molecular Systems Biology, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich,8093 Zurich, Switzerland; Division of Biosciences, Institute of Structural andMolecular Biology, University College London (UCL), London WC1E 6BT, UK; Co-firstauthor
| Graphical Abstract
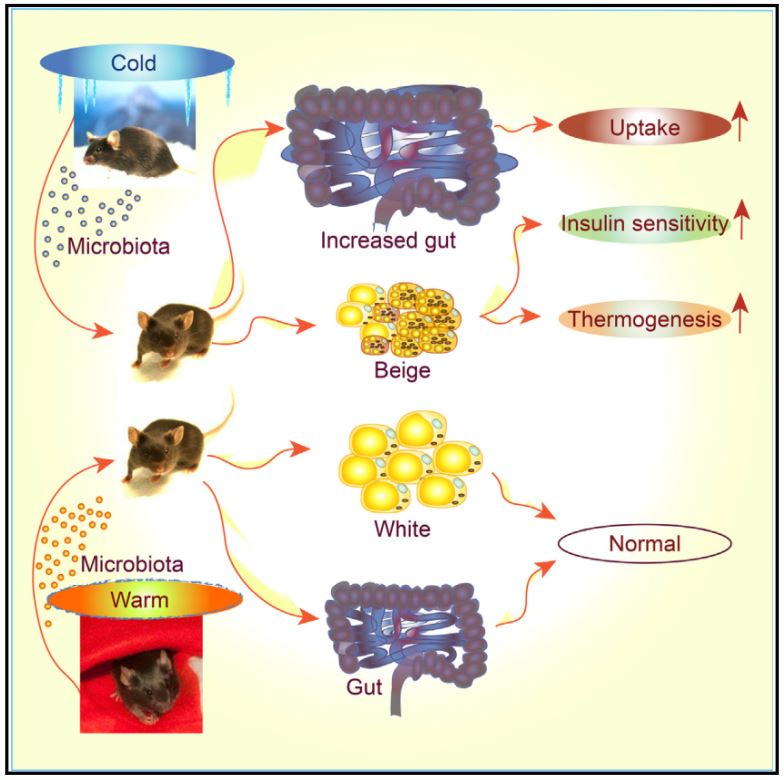
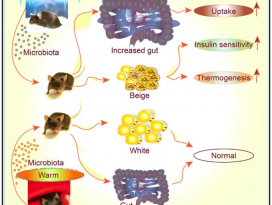
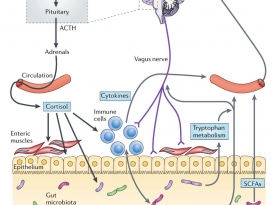
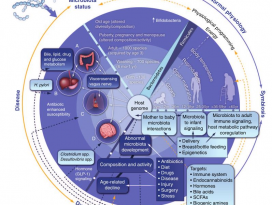
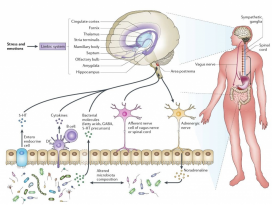
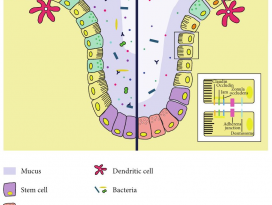
In Brief Cold exposure markedly shifts the composition of the gut microbiota. This ‘‘cold microbiota’’ mediates remodeling of the fat and intestinal tissues, helping the host to withstand periods of high energy demand. Highlights - Cold exposure leads to marked changes in the gut microbiota composition - Cold microbiota transplantation increases insulin sensitivity and WAT browning - Cold exposure or cold transplantation increase the gut size and absorptive capacity - Reconstitution of cold-suppressed A. muciniphila reverts the increased caloric uptake SUMMARY Microbial functions in the host physiology are a result of the microbiota-host co-evolution. We show that cold exposure leads to marked shift of the microbiota composition, referred to as cold microbiota. Transplantation of the cold microbiota to germ-free mice is sufficient to increase insulin sensitivity of the host and enable tolerance to cold partly by promoting the white fat browning, leading to increased energy expenditure and fat loss. During prolonged cold, however, the body weight loss is attenuated, caused by adaptive mechanisms maximizing caloric uptake and increasing intestinal, villi, and microvilli lengths. This increased absorptive surface is transferable with the cold microbiota, leading to altered intestinal gene expression promoting tissue remodeling and suppression of apoptosis—the effect diminished by co-transplanting the most cold-downregulated strain Akkermansia muciniphila during the cold microbiota transfer. Our results demonstrate the microbiota as a key factor orchestrating the overall energy homeostasis during increased demand. |
제목
장내 미생물은 추운 환경에서 에너지 항상성을 조율한다.
내용
개요
추운 환경에 노출되면 장내 미생물의 구성이 현저히 변화된다. 일명 '차가운 미생물(cold microbiota)'은 지방과 장 조직의재구성을 매개하여, 숙주로 하여금 많은 에너지가 요구되는 기간을 견딜 수 있도록 돕는다.
하이라이트
- 추운 환경으로의 노출은 장내 미생물 구성의 두드러진 변화를 가져온다.
- ‘차가운 미생물’의 이식은 인슐린 민감도를 증가시키고, 백색지방조직(WAT)이 갈색지방조직(BAT)화 되는 것 (WAT browning)을 증가시킨다.
- 추위 노출 또는 차가운 미생물 이식은 장의 크기와 흡수 능력을 증대시킨다.
- 추위를 억제하는 아커만시아 무시니필라 (A. muciniphila)가 재구성되어 증가하면 칼로리 흡수 증가가 억제된다.
요약
숙주 생리학에서의 미생물의 기능은 미생물과 숙주가 공동 진화한 결과이다. 추위에대한 노출은 ‘차가운 미생물’이라 일컬어지는 미생물 구성의두드러진 변화를 가져온다는 것을 보여준다. 차가운 미생물을 무균 쥐에 이식하면 숙주의 인슐린 민감도를충분히 높이고, 백색지방의 갈변을 촉진하여 추위에 견디는 신체 부분이 생성되도록 하고, 이는 에너지 소비와 지방 감소의 증가로 이어진다. 그러나 장기간지속되는 추위에서의 체중 감량은 열량 흡수를 최대화하고 장, 융모 및 미생물의 길이를 증가시키는 적응메커니즘에 의해 약화된다. 이러한 흡수 표면의 증가는 차가운 미생물에 의해 전이되며, 이는 장의 유전자 발현이 변형되도록 하여 조직 재구성을 촉진하고 세포 사멸을 억제한다. 차가운 미생물 이식 과정에서 추위를 가장 하향 조절하는 균주인 아커만시아 무시니필라 (Akkermansia muciniphila)를공동 이식함으로써 상기 영향은 감소한다. 본 연구의 결과는 미생물이 수요 증가 기간 동안 전반적인 에너지항상성을 조율하는 핵심 요소로서 기능함을 증명한다.
Keywords
: #ColdExposure #Microbiome#Microorganisms#Microbes #Microbiota #GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota#GutMicrobes #ColdMicrobiota# ColdMicrobiotaTransplantation #WAT #WhiteAdiposeTissue #WhiteFat#WhiteFatBrowning #WATBrowning #BAT #BrownAdiposeTissue #Probiotics #Homeostasis #EnergyHomeostasis#AkkermansiaMuciniphila #A. muciniphila
#추위 #추위노출 #추위환경노출 #마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군 #차가운미생물 #콜드미생물 #차가운미생물이식 #콜드미생물이식 #백색지방조직 #백색지방 #백색지방갈변 #갈색지방 #갈색지방조직 #프로바이오틱스 #유익균 #항상성 #에너지항상성 #아커만시아무시니필라 #A.무시니필라
[출처: Chevalier,C., Stojanović, O., Colin, D. J., Suarez-Zamorano, N., Tarallo, V.,Veyrat-Durebex, C., ... & Montet, X. (2015). Gut microbiota orchestratesenergy homeostasis during cold. Cell, 163(6), 1360-1374.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.