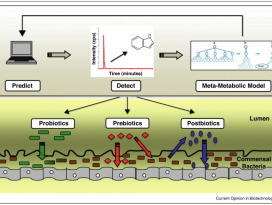
Postbiotics: what else?
K. Tsilingiri andM. Rescigno
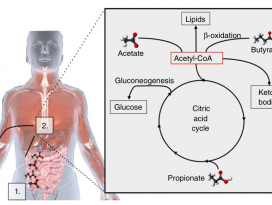
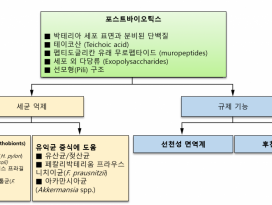
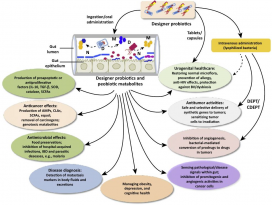
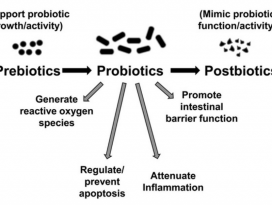
| Abstract The use of probiotics and synbiotics in the food industry or as food supplements for a balanced diet and improved gut homeostasis has been blooming for the past decade. As feedback from healthy consumers is rather enthusiastic, a lot of effort is currently directed in elucidating the mechanisms of interaction between beneficial microbes and barrier and immune function of the host. The use of probiotics or synbiotics for treating certain pathologies has also been examined, however, the outcome has not always been favourable. In most cases, the effect of the administered probiotic is evident when the bacteria are still alive at the time they reach the small and large intestine, suggesting that it is dependent on the metabolic activity of the bacteria. Indeed, in some occasions it has been shown that the culture supernatant of these bacteria mediates the immunomodulatory effect conferred to the host. Recent work on relevant probiotic strains has also led to the isolation and characterisation of certain probiotic-produced, soluble factors, here called postbiotics, which were sufficient to elicit the desired response. Here, we summarise these recent findings and propose the use of purified and well characterised postbiotic components as a safer alternative for clinical applications, especially in chronic inflammatory conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, where probiotics have not yet given encouraging results as far as induction of remission is concerned. |
제목
포스트바이오틱스, 그 밖에는?
내용
지난 10년간 식품 또는 식품 보충제 산업에서 프로바이오틱스와 신바이오틱스(synbiotics)를 균형 잡힌 식단과 장내 항상성 (guthomeostasis)의 개선을 위해 사용하기 시작했다. 건강한 소비자로부터의 피드백이다소 열렬하기 때문에, 유익균, 장벽, 숙주의 면역 기능 사이의 상호 작용 메커니즘을 밝히는 데 많은 노력을 기울이고 있다. 특정 병리를 치료하기 위한 프로바이오틱스 또는 신바이오틱스의 사용이 검토되어왔지만, 연구 결과가 항상 좋은 것은 아니다. 대부분의 경우에서 투여된 프로바이오틱스의효과는 박테리아가 소장 및 대장에 도달하는 시점에 계속 살아있을 때에 명확해지며, 이는 박테리아의 대사활동에 의존한다는 것을 암시한다. 실제로, 어떤 경우에는이러한 박테리아의 배양상층액 (culture supernatant)이 숙주에게 부여된 면역 조절 효과를매개하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 관련된 프로바이오틱스 균주에 대한 최근의 연구는 특정 프로바이오틱스에서생성된 용해성 인자의 분리 및 특성 분석을 이끌어 냈으며, 해당 인자는 원하는 생물 반응을 이끌어 내기에충분하며 포스트바이오틱스 (postbiotics)라고 불린다. 해당본문에서 우리는 최근의 연구 결과들을 요약하고 임상 응용, 특히 프로바이오틱스가 증상 완화를 유도하는것에 관해 아직까지 고무적인 결과를 내지 못하고 있는 염증성 장질환과 같은 만성 염증질환을 위해 보다 안전한 대안으로서 정제되고 잘 특성화 된포스트바이오틱스 성분의 사용을 제안한다.
Keywords
: #Probiotics #Synbiotics #Postbiotics#Metabolites #MetabolicActivity #Homeostasis #GutHomeostasis#BeneficialMicrobes #Microbiome #Microorganisms #Microbes #Microbiota#GutMicrobiome #GutMicrobiota #GutMicrobes
#프로바이오틱스 #유산균 #유익균#신바이오틱스 #포스트바이오틱스 #대사산물 #대사활동 #항상성#장내항상성 #8515 #마이크로바이옴 #미생물총 #미생물군 #미생물유전자 #장내미생물 #장내미생물총 #장내미생물군
[출처: Tsilingiri, K., & Rescigno, M. (2012).Postbiotics: what else?. Beneficial microbes, 4(1), 101-107.]
|
| ㈜마이크로바이옴 ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 최고의 기술력을 바탕으로 마이크로바이옴 산업의 성장과 발전의 선도적 역할을 하고 있는 대한민국 대표 마이크로바이옴 R&D 전문 기업입니다. ㈜마이크로바이옴은 생명공학 국가연구기관인 한국생명공학연구원과 마이크로바이옴 관련 상품에 대하여 공동연구개발 및 기술이전을 통하여 공동특허 출원과 마이크로바이옴 상품화에 성공하였고, 마이크로바이옴 글로벌 기업이 되기 위하여 연구개발을 지속하고 있습니다. |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.