[Saccharomyces cerevisiae] Saccharomyces cerevisiae Modulates Immune Gene Expressions and Inhibits ETEC-Mediated ERK1/2 and p38 Signaling Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cell
- e 2403
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Modulates Immune Gene Expressions and Inhibits ETEC-Mediated ERK1/2 and p38 Signaling Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cell
Galliano Zanello1,2, Mustapha Berri2, Joe ¨lle Dupont3, Pierre-Yves Sizaret4, Romain D’Inca1, Henri Salmon2., Franc¸ois Meurens2*.
Abstract
mortality. Administration of probiotics as feed additives displayed health benefits against intestinal infections. Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc) is non-commensal and non-pathogenic yeast used as probiotic in gastrointestinal diseases. However, the immuno- modulatory effects of Sc in differentiated porcine intestinal epithelial cells exposed to ETEC were not investigated.
recruitment and activation of immune cells in differentiated porcine intestinal epithelial IPEC-1 cells. We demonstrated that viable Sc inhibits the ETEC-induced expression of pro-inflammatory transcripts (IL-6, IL-8, CCL20, CXCL2, CXCL10) and proteins (IL-6, IL-8). This inhibition was associated to a decrease of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation, an agglutination of ETEC by Sc and an increase of the anti-inflammatory PPAR-c nuclear receptor mRNA level. In addition, Sc up-regulates the mRNA levels of both IL- 12p35 and CCL25. However, measurement of transepithelial electrical resistance displayed that Sc failed to maintain the barrier integrity in monolayer exposed to ETEC suggesting that Sc does not inhibit ETEC enterotoxin activity.
Sc (strain CNCM I-3856) displays multiple immuno-modulatory effects at the molecular level in IPEC-1 cells suggesting that Sc may influence intestinal inflammatory reaction. |
제목 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Modulates Immune Gene Expressions and Inhibits ETEC-Mediated ERK1/2 and p38 Signaling Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cell 내용 Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) 감염은 전 세계적으로 돼지 산업에서 큰 경제적 손실을 초래한다. ETEC 감염은 장 상피 세포에서 염증 반응을 일으켜 성장률의 감소와 사망을 일으키는 돼지의 설사를 유발시킨다. 사료 첨가제로서의 프로바이오틱스의 투여는 장 감염에 대한 건강상의 이점을 나타냈다. Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc)는 위장병에서 프로바이오틱스로 사용되는 비 공생성 및 비 병원성 효모이다. 그러나, ETEC에 노출 된 분화 된 돼지 장 상피 세포에서 Sc의 면역 조절 효과는 조사되지 않았다. 우리는 효모 Sc (CNCM I-3856 균주)가 분화된 돼지의 장 상피 세포 IPEC-1에서 면역 세포의 염증, 모집 및 활성화에 관여하는 전사 및 단백질 발현을 조절한다고 보고했다. 우리는 Sc가 ETEC에 의해 유발된 염증 전 사체 (IL-6, IL-8, CCL20, CXCL2, CXCL10)와 단백질 (IL-6, IL-8)의 발현을 억제한다는 것을 증명했다. 이 억제는 ERK1 / 2 및 p38 MAPK 인산화의 감소, Sc에 의한 ETEC의 응집 및 항 염증 PPAR-c 핵 수용체 mRNA 수준의 증가와 관련이 있다. 또한 Sc는 IL-12p35와 CCL25의 mRNA 수준을 상향 조절한다. 그러나, 상피 전기 저항의 측정은 Sc가 ETEC에 노출된 단일 층에서 장벽 완전성을 유지하는데 실패하여 Sc가 ETEC 장 독소 활성을 억제하지 않는다는 것을 암시한다. 결론적으로 Sc (CNCM I-3856 균주)는 IPEC-1 세포에서 분자 수준에서 다중 면역 조절 효과를 나타내어 Sc가 장 염증 반응에 영향을 줄 수 있음을 시사한다. [출처 : PLoS ONE April 2011 | Volume 6 | Issue 4 | e18573] |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
| 20 | 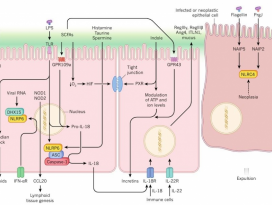 | 2082 | |
| 19 | 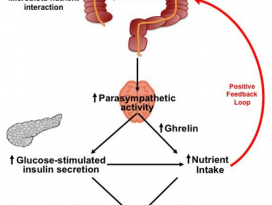 | [Gut Microbiome] Acetate mediates a microbiome–brain–β cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome | 2202 |
| 18 | 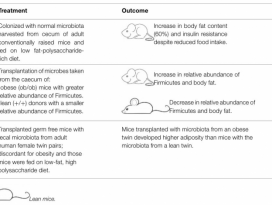 | 2031 | |
| 17 | 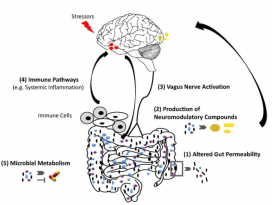 | [Gut Microbiome] The Gut Microbiome in Human Neurological Disease: A Review | 2536 |
| 16 |  | [Gut Microbiome] Rapidly expanding knowledge on the role of the gut microbiome in health and disease | 2180 |
| 15 |  | 2222 | |
| 14 |  | 2415 | |
| 13 |  | 2359 | |
| 12 |  | 2441 | |
| 11 |  | 2459 | |
| 10 |  | [Bacillus] Anti-influenza Activity of a Bacillus subtilis Probiotic Strain | 2119 |
| 9 |  | [Bacillus] Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1 isolated from pistachio nuts of Iran | 2272 |
| 8 |  | 2349 | |
| 7 |  | 3239 | |
| 6 |  | 2125 | |
| 5 |  | 2340 | |
| 4 |  | 2297 | |
| 3 |  | 2112 | |
| 2 |  | 2077 | |
| 1 |  | 2403 |
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.