[Lactobacillus paracasei] Effect of LactobacillusparacaseiST11 on a nasal provocation test with grass pollen in allergic rhinitis
- e 2360
Effect of LactobacillusparacaseiST11 on a nasal provocation test with grass pollen in allergic rhinitis
J. Wassenberg1, S. Nutten2, R. Audran1, N. Barbier1, V. Aubert1, J. Moulin2, A. Mercenier2 and F. Spertini1
Abstract
dermatitis. However, few studies exist that document their efficacy for upper airways allergies such as allergic rhinitis. ObjectiveToinvestigatetheeffectofshort-termoraladministrationofLactobacillusparacasei ST11 on a nasal provocation test (NPT) with grass pollen. Methods Thirty-one adult volunteers with allergic rhinitis were enrolled in a randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled study, based on two 4-week cross-over periods of product consumption (ST11-fermented milk vs. placebo), separated by a wash-out period of 6–8 weeks. Objective and subjective clinical parameters of NPTas well as systemic and nasal immunological parameters were compared between the two treatment periods (registration number: NCT 011 50 253). Results Subjects that received ST11-fermented milk had lower nasal congestion than subjects under placebo (visual analogical scale; Po0.05). Nasal pruritus followed the same trend. However, no significant change in combined nasal reaction threshold was observed between the two periods. IL-5 secretion by peripheral blood mononuclear cells and serum allergenspecific IgG4 were significantly lower in ST11- fermented milk group compared to placebo group. IL-8 and IL-10 secretion followed the same trend. Conclusion and Clinical Relevance Short-term treatment with ST11-fermented milk before NPT significantly improved a clinical marker of NPT (subjective nasal congestion) and downregulatedsystemicimmunemarkers(IL-5fromperipheralbloodmononuclearcellsandserum IgG4). These data strongly suggest that probiotics may down modulate key parameters of allergic rhinitis and warrant future evaluation in seasonal trials.
|
제목 Effect of LactobacillusparacaseiST11 on a nasal provocation test with grass pollen in allergic rhinitis 내용 프로바이오틱스는 아토피성 피부염과 같은 아토피성 질환의 예방 및 개선과 관련이 있습니다. 그러나 알레르기성 비염과 같은 상부기도 알레르기에 대한 효능을 문서화 한 연구는 거의 없다. 꽃가루로 비강 자극 검사 (NPT)에 Lactobacillus paracasei ST11의 단기 경구 투여 효과를 조사하였다. 알레르기 비염을 앓고 있는 31명의 성인 자원 봉사자가 제품 소비 (ST11 발효 우유 VS 위약)의 2회 4주 교차 실험 기간에 근거하여 무작위, 이중 맹검, 위약 대조 연구에 등록되었으며, 6주에서 8주 사이에는 투여를 중단 시킴으로써 구분지었다. ST11 발효유를 섭취 한 대상자는 위약군보다 비강 충혈이 낮았다 (시각적 유사도; P <0.05). 비강 가려움증도 같은 경향을 보였다. 그러나 두 기간 사이에 비강 내 반응 역치의 유의 한 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 말초 혈액 단핵구와 혈청 알레르기 항원 특이 IgG4에 의한 IL-5 분비는 ST11 발효유 군에서 위약군에 비해 유의하게 낮았다. IL-8 및 IL-10 분비는 동일한 경향을 따랐다. NPT 전에 ST11 발효유를 단기간 투여하면 NPT (주관적 비강 울혈) 및 전신 면역 마커 (말초 혈액 단핵구와 혈청 IgG4에서 IL-5)의 임상적 표지가 크게 개선되었다. 이러한 데이터는 프로바이오틱스가 알레르기성 비염의 핵심 매개 변수를 낮게 조정하고 계절적인 시험에 대한 미래의 평가를 보증 할 수 있음을 강력히 시사한다. [출처 : 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 41:565–573 ] |
| no. | 제목 | 조회수 |
|---|
| 20 | 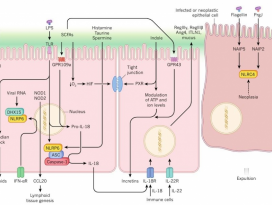 | 2082 | |
| 19 | 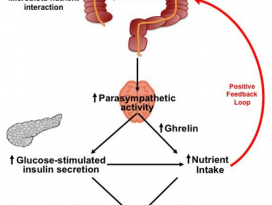 | [Gut Microbiome] Acetate mediates a microbiome–brain–β cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome | 2203 |
| 18 | 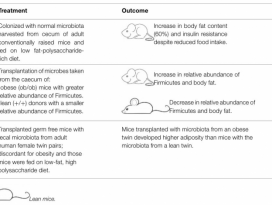 | 2032 | |
| 17 | 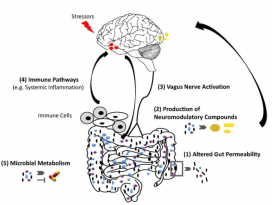 | [Gut Microbiome] The Gut Microbiome in Human Neurological Disease: A Review | 2536 |
| 16 |  | [Gut Microbiome] Rapidly expanding knowledge on the role of the gut microbiome in health and disease | 2180 |
| 15 |  | 2222 | |
| 14 |  | 2415 | |
| 13 |  | 2360 | |
| 12 |  | 2441 | |
| 11 |  | 2459 | |
| 10 |  | [Bacillus] Anti-influenza Activity of a Bacillus subtilis Probiotic Strain | 2119 |
| 9 |  | [Bacillus] Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1 isolated from pistachio nuts of Iran | 2273 |
| 8 |  | 2349 | |
| 7 |  | 3239 | |
| 6 |  | 2125 | |
| 5 |  | 2340 | |
| 4 |  | 2297 | |
| 3 |  | 2112 | |
| 2 |  | 2077 | |
| 1 |  | 2403 |
㈜마이크로바이옴 ㅣ 서울시 서대문구 연희로 77-12 영화빌딩2층
Tel :02-322-0302 l Fax : 02-322-0759
Copyright (c) Microbiome. Co. All Rights Reserved.